The overall structure of the project’s work plan consists of 5 Work Packages (WP) shown in Figure 1. In particular:
1. WP1: extensive literature review and determination of the state of the art concerning the available technologies, overall design of the system. Outcome: report on the state of the art and project’s system plan.
2. WP2 (Simulation Phase): At the middle of WP1, ML and SRT algorithms development phase along with simulations using XrayImagingSimulator, will start to ensure that all needed data will be available for the development of the algorithms. A milestone at the middle of WP2 when a first version of the algorithms will be ready and tested based only on simulation data. At this point, the CUDA (GPU) version of the developed algorithms will also start. Outcomes: software phantoms, (some designed to be also physically built), the developed of refined and validated via simulation algorithms, based on initial application results from (WP3).
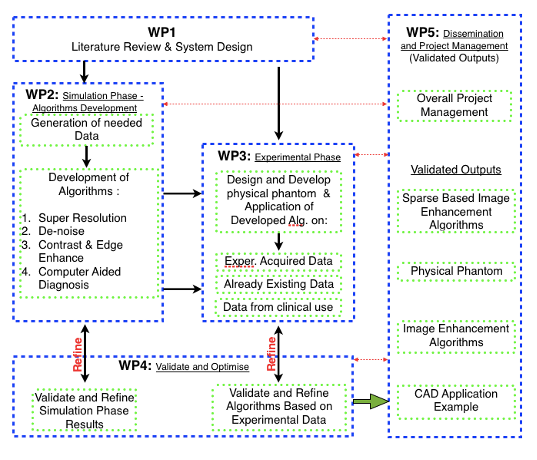
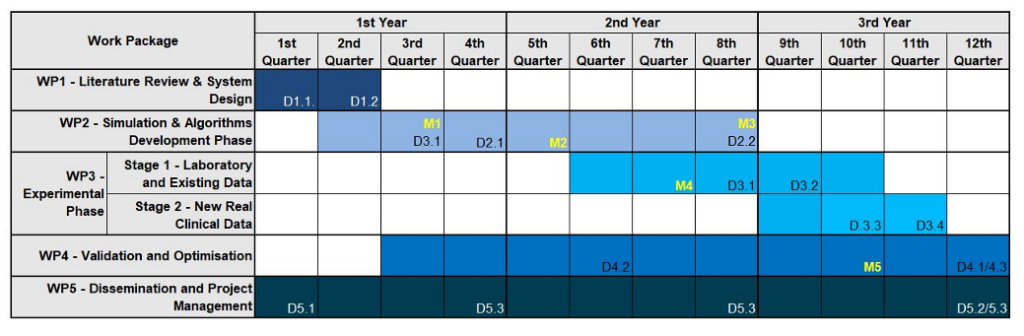
3. WP3 (Experimental Phase): begins in the middle of (WP2) where, a first version of all the proposed algorithms will be available along with the software phantoms. In Stage 1 of WP3 actual physical phantoms will be created using conventional and 3D printing techniques and will be used for x-ray imaging. The algorithms will then be applied on the produced experimental data and, based on the outputs, the algorithms will be refined. The CAD’s system training will be refined using all the labelled experimental data produced. Algorithms will be also applied in existing data from previous collaborations and experiments of the BITU team and PI in Elettra synchrotron facilities and from collaborating hospitals. In the 2nd stage of WP3 new real clinical data will be acquired. All image enhancement algorithms will be tested and validated using these data, and all necessary improvements will be done. The ML CAD system, will now enter its final training phase, where after the successive augmented training starting with simulated and then experimental data, will be now fed and trained using labelled real clinical data from available open access mammographic datasets (Moreira et al., 2012) (Suckling et al., 2015) along with data available in the BITU team and collaborating hospitals. An evaluation study will take place where images will be given to experts to analyse them and comparison with the ML CAD outputs. Outputs: physical phantoms, experimental data and algorithms tested, refined and retrained with real data.
4. WP4 (Validation and Optimization): Follows the beginning of WP2, a continuous Validation and Optimization procedure will run in parallel with WP2 and WP3 until the end of the project. All the produced algorithms and data will be validated and, when appropriate, redesigned and refined. This approach has been chosen in order to make sure that any problem that may occur, will be detected and all needed actions will be done at an early stage. Running of WP4 in parallel from the beginning of the project, will also allow the direct comparison of the results acquired by the simulation and experimental phases and switching from simulation to experiments and vice versa in order to validate and refine the produced algorithms. This continuous monitoring and evaluation will ensure the positive outcome of the project. Output: final versions of the derived algorithms.
5. WP5 (Dissemination & Management): dissemination actions such as paper submission in international peer reviewed journals, conferences and presentation of work, along with a web site of the Project. A Workshop on project’s outputs and related scientific fields will take place in the facilities of Patras University, with invited researchers from Greece and EU. Project management will take place in WP5 and will be running s throughout the whole duration of the project.